cast iron tig welding rod
ఫిబ్ర . 14, 2025 16:17
Welding stainless steel (SS) rods has always been a subject of interest for both novice and seasoned welders. Stainless steel's unique properties, including its resistance to rust and high temperature, make it a popular choice in many industries. This article explores the intricacies of welding SS rods, combining personal experience with professional insights to provide a guide that stands out in the crowded space of SEO content.
Filler material selection is equally important in achieving a successful weld. The filler rod must be compatible with the base metal to prevent corrosion and cracking. For austenitic stainless steels, a 308 or 309 grade filler is normally recommended. These fillers contain high chromium and nickel content, contributing to the durability and strength of the weld. In terms of PPE (Personal Protective Equipment), always prioritize safety. Stainless steel welding produces harmful fumes and requires adequate ventilation. Wearing protective clothing, gloves, and face shields is essential to avoid burns and injuries. A respirator designed to filter out metal fumes is also recommended to protect against inhaling hazardous particles. Understanding the specific application and environment of the final product is essential when performing any welding task with SS rods. Environments with exposure to high chloride concentrations or marine settings demand higher corrosion resistance—a factor to consider when selecting both stainless steel grades and filler materials. In my years of experience, ensuring weld quality through testing is an often-overlooked step. Conducting non-destructive testing (NDT) such as X-ray or ultrasonic inspection can verify weld integrity, identifying potential weaknesses without damaging the component. This not only enhances the reliability of the weld but also builds trust with clients seeking long-lasting solutions. Despite the complexities involved in welding stainless steel rods, mastering the process significantly broadens one’s welding skills, offering opportunities across various industries, from construction to automotive applications. As this guide outlines, achieving exceptional results relies on a thorough understanding of materials, techniques, and safety measures. By prioritizing these elements, professionals can confidently produce high-quality, durable welds, setting themselves apart as experts in the field.
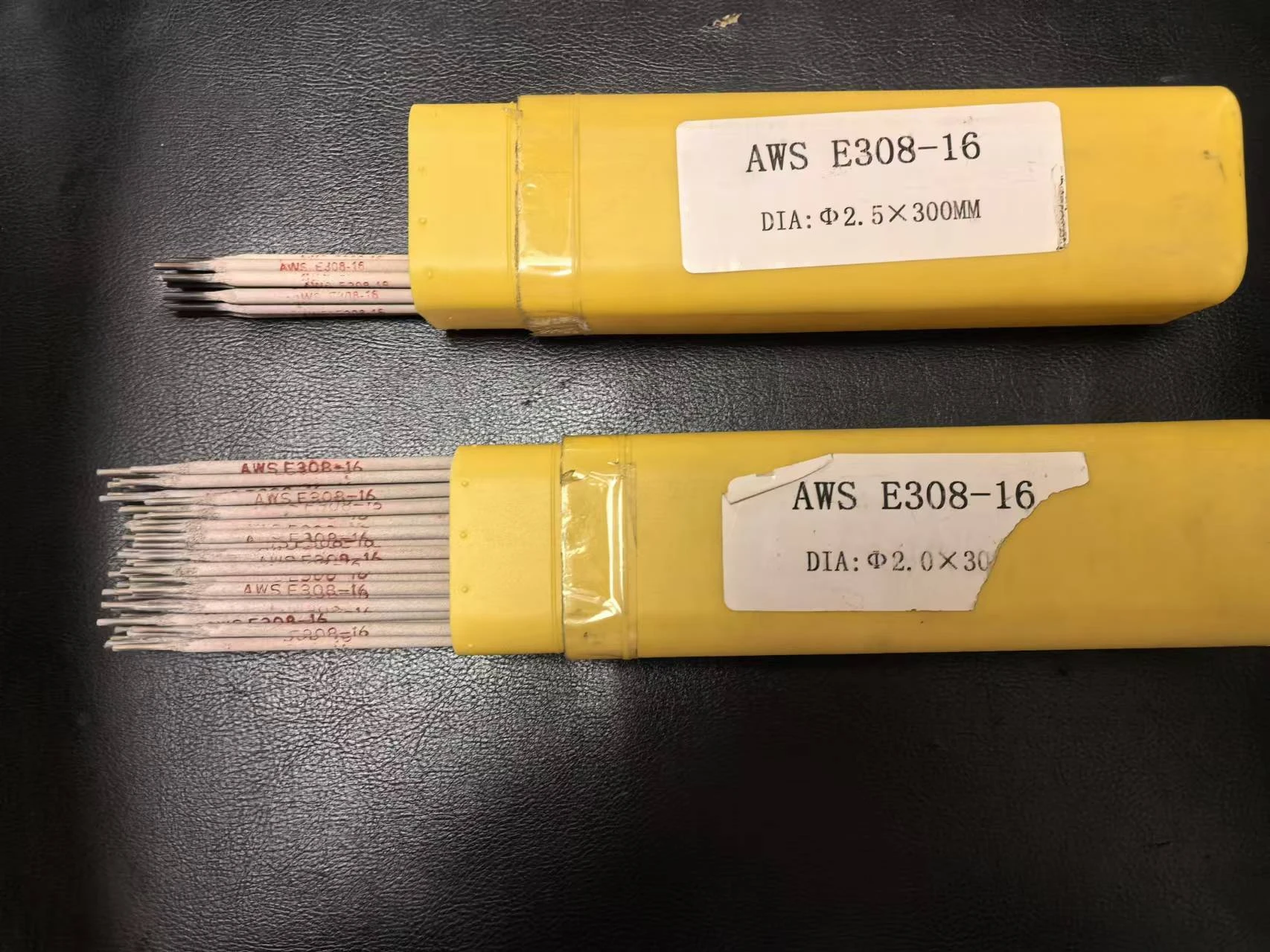

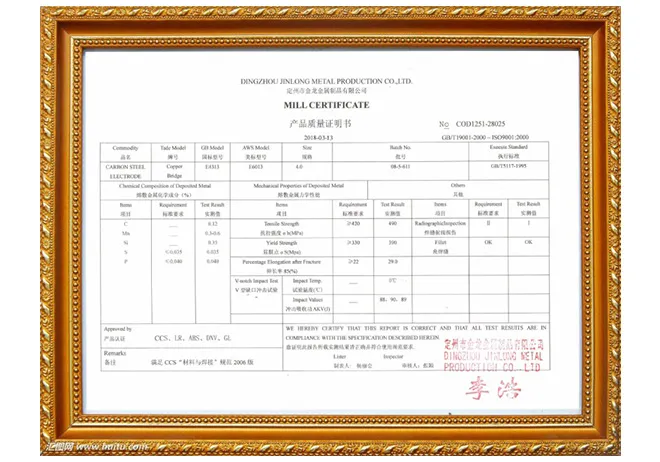
Filler material selection is equally important in achieving a successful weld. The filler rod must be compatible with the base metal to prevent corrosion and cracking. For austenitic stainless steels, a 308 or 309 grade filler is normally recommended. These fillers contain high chromium and nickel content, contributing to the durability and strength of the weld. In terms of PPE (Personal Protective Equipment), always prioritize safety. Stainless steel welding produces harmful fumes and requires adequate ventilation. Wearing protective clothing, gloves, and face shields is essential to avoid burns and injuries. A respirator designed to filter out metal fumes is also recommended to protect against inhaling hazardous particles. Understanding the specific application and environment of the final product is essential when performing any welding task with SS rods. Environments with exposure to high chloride concentrations or marine settings demand higher corrosion resistance—a factor to consider when selecting both stainless steel grades and filler materials. In my years of experience, ensuring weld quality through testing is an often-overlooked step. Conducting non-destructive testing (NDT) such as X-ray or ultrasonic inspection can verify weld integrity, identifying potential weaknesses without damaging the component. This not only enhances the reliability of the weld but also builds trust with clients seeking long-lasting solutions. Despite the complexities involved in welding stainless steel rods, mastering the process significantly broadens one’s welding skills, offering opportunities across various industries, from construction to automotive applications. As this guide outlines, achieving exceptional results relies on a thorough understanding of materials, techniques, and safety measures. By prioritizing these elements, professionals can confidently produce high-quality, durable welds, setting themselves apart as experts in the field.
Related Video
Copyright © 2025 Dingzhou Jinlong Metal Production Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sitemap | Privacy Policy




























