steel rod welding
Feb . 12, 2025 17:45
Steel rod welding is an intricate process that plays a critical role in various industrial and construction applications. This technique requires not only skilled labor but also a comprehensive understanding of materials, weld types, and safety standards. With the advancement of technology and evolving industry requirements, the methods used in steel rod welding have become more refined, allowing for enhanced efficiency and stronger welds.
Professionalism and expertise are highlighted through continuous training and certification. Welding, being an ever-evolving field, benefits greatly from ongoing education. Welders who engage in continuous learning and skill advancement offer superior craftsmanship and are better equipped to adapt to new technologies and methods. Certifications from recognized bodies not only attest to a welder's skillset but also boost client confidence and are often prerequisites for high-profile projects. Advancements in technology have also significantly influenced steel rod welding practices. The introduction of automated and robotic welding systems has revolutionized the industry by increasing precision and efficiency. These systems help in maintaining consistency in weld quality, especially in mass production scenarios. However, they also require skilled operators who understand both the nuances of welding techniques and the complexities of automated systems. To effectively manage resources and project timelines, many companies are leveraging digital tools and software in their welding operations. Such tools can optimize weld paths, predict material costs, and schedule regular maintenance to prevent equipment downtimes. Embracing digital transformation within welding processes ensures that companies stay ahead in terms of efficiency and competitiveness. In conclusion, steel rod welding is a complex art that demands a balance between human skill and technological advancement. Selecting appropriate materials, mastering diverse welding techniques, ensuring stringent safety measures, and fostering continuous professional development are all pivotal. As industries continue to grow and demand more durable and reliable structures, the role of innovation in welding processes becomes even more significant. By prioritizing these elements, companies can achieve superior welding outcomes that offer long-lasting performance and reliability.
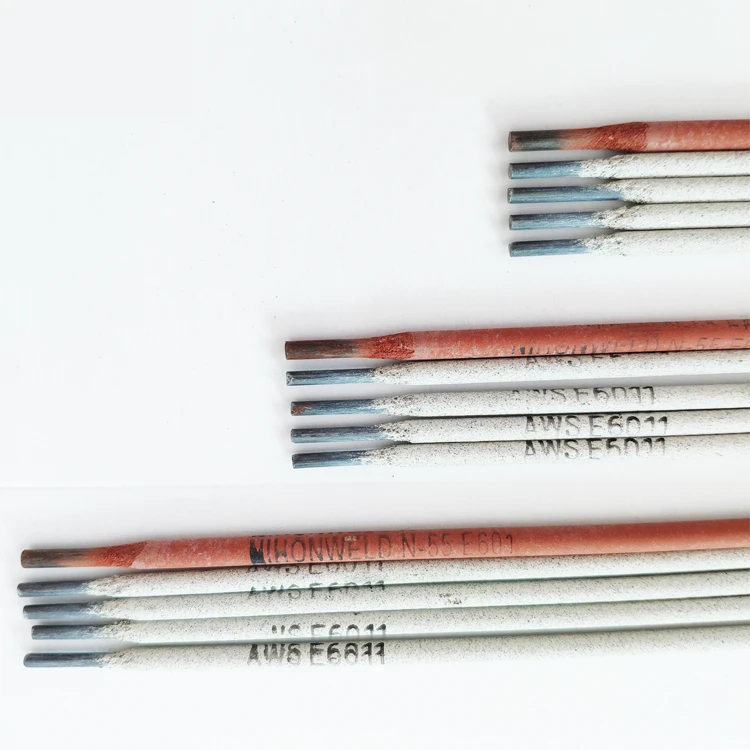

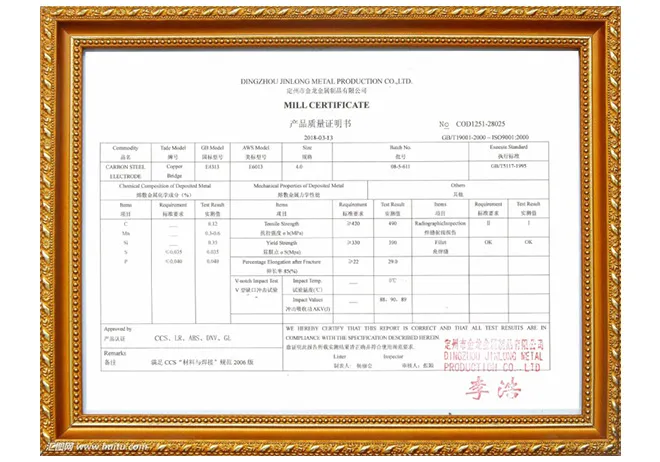
Professionalism and expertise are highlighted through continuous training and certification. Welding, being an ever-evolving field, benefits greatly from ongoing education. Welders who engage in continuous learning and skill advancement offer superior craftsmanship and are better equipped to adapt to new technologies and methods. Certifications from recognized bodies not only attest to a welder's skillset but also boost client confidence and are often prerequisites for high-profile projects. Advancements in technology have also significantly influenced steel rod welding practices. The introduction of automated and robotic welding systems has revolutionized the industry by increasing precision and efficiency. These systems help in maintaining consistency in weld quality, especially in mass production scenarios. However, they also require skilled operators who understand both the nuances of welding techniques and the complexities of automated systems. To effectively manage resources and project timelines, many companies are leveraging digital tools and software in their welding operations. Such tools can optimize weld paths, predict material costs, and schedule regular maintenance to prevent equipment downtimes. Embracing digital transformation within welding processes ensures that companies stay ahead in terms of efficiency and competitiveness. In conclusion, steel rod welding is a complex art that demands a balance between human skill and technological advancement. Selecting appropriate materials, mastering diverse welding techniques, ensuring stringent safety measures, and fostering continuous professional development are all pivotal. As industries continue to grow and demand more durable and reliable structures, the role of innovation in welding processes becomes even more significant. By prioritizing these elements, companies can achieve superior welding outcomes that offer long-lasting performance and reliability.
Related Video
Copyright © 2025 Dingzhou Jinlong Metal Production Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sitemap | Privacy Policy




























