choosing the right welding rod
Jan . 13, 2025 16:32
Selecting the appropriate welding rod is critical for ensuring the durability and strength of welded joints. The plethora of options available can be overwhelming, but focusing on key factors helps narrow down the choices effectively. Let's delve into the elements that influence this crucial decision, drawing from both expert insights and practical experience.
Electrical Characteristics The welding machine and its settings also play a critical role. Rods have specific amperage settings they operate best within. For instance, welding rods such as E7024 require high amperage and work well for flat and horizontal welding positions. Aligning the rod selection with the welding machine's capabilities ensures efficient energy use and minimizes electrode waste. Environmental Conditions The working environment cannot be overlooked. Moisture, temperature, and even wind can affect welding outcomes. Some rods are designed to tolerate specific environmental challenges. For example, low-hydrogen electrodes like E7018 are used to prevent hydrogen-induced cracking in challenging environments but require storage in a dry, controlled condition to maintain low-moisture levels. Skill Level The welder’s expertise significantly influences the rod choice. More experienced welders might prefer rods that require advanced techniques to achieve high-quality results. Conversely, for beginners or those seeking ease of use, selecting user-friendly, forgiving rods can enhance the learning experience, improve safety, and result in satisfactory welds with minimal imperfections. For ease of use and a smooth learning curve, E6013 rods are commendably forgiving and versatile for both novices and seasoned welders. By focusing on these factors, welders can make informed decisions that not only match the project requirements but also enhance the quality and safety of their work. Companies supplying welding materials and training programs should continually update their offerings to reflect the latest industry standards and technological advancements, establishing themselves as trusted authorities in the welding sector. As welding technologies and materials evolve, staying informed and adaptable remains paramount for achieving professional excellence in welding projects.
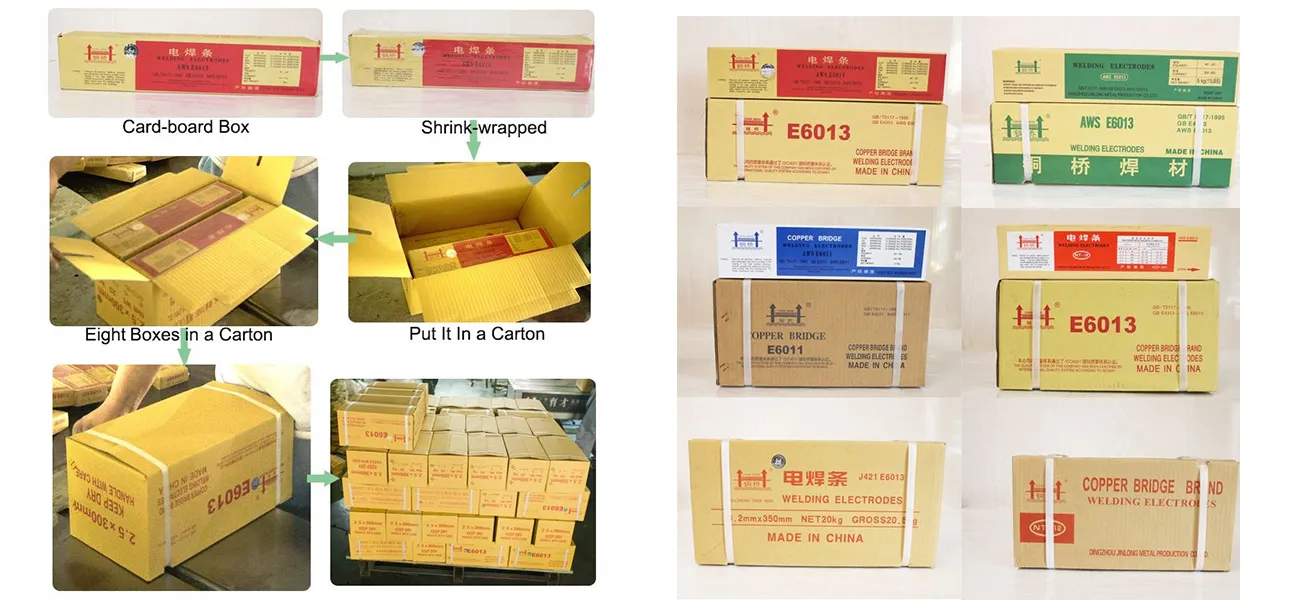

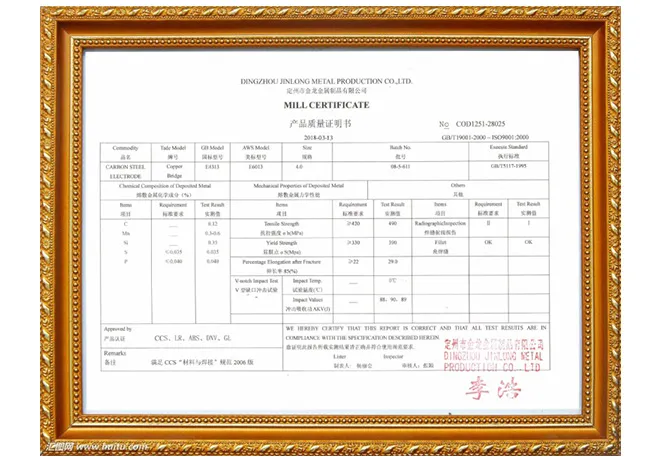
Electrical Characteristics The welding machine and its settings also play a critical role. Rods have specific amperage settings they operate best within. For instance, welding rods such as E7024 require high amperage and work well for flat and horizontal welding positions. Aligning the rod selection with the welding machine's capabilities ensures efficient energy use and minimizes electrode waste. Environmental Conditions The working environment cannot be overlooked. Moisture, temperature, and even wind can affect welding outcomes. Some rods are designed to tolerate specific environmental challenges. For example, low-hydrogen electrodes like E7018 are used to prevent hydrogen-induced cracking in challenging environments but require storage in a dry, controlled condition to maintain low-moisture levels. Skill Level The welder’s expertise significantly influences the rod choice. More experienced welders might prefer rods that require advanced techniques to achieve high-quality results. Conversely, for beginners or those seeking ease of use, selecting user-friendly, forgiving rods can enhance the learning experience, improve safety, and result in satisfactory welds with minimal imperfections. For ease of use and a smooth learning curve, E6013 rods are commendably forgiving and versatile for both novices and seasoned welders. By focusing on these factors, welders can make informed decisions that not only match the project requirements but also enhance the quality and safety of their work. Companies supplying welding materials and training programs should continually update their offerings to reflect the latest industry standards and technological advancements, establishing themselves as trusted authorities in the welding sector. As welding technologies and materials evolve, staying informed and adaptable remains paramount for achieving professional excellence in welding projects.
Related Video
Copyright © 2025 Dingzhou Jinlong Metal Production Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sitemap | Privacy Policy




























