copper coated mild steel
فوریه . 15, 2025 04:37
Hardfacing stainless steel, a specialized welding process designed to extend the life of metallic parts, has found its pivotal role in enhancing durability and reducing wear in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace. This article delves into the intricacies of hardfacing stainless steel, offering insights from hands-on experiences, professional expertise, authoritative sources, and trustworthy practices.
To establish authoritativeness in hardfacing stainless steel, it's crucial to rely on industry standards and guidelines, such as those provided by the American Welding Society (AWS). Compliance with these standards ensures not only the quality and safety of the hardfacing application but also enhances its performance. Documentation and adherence to these guidelines demonstrate a commitment to best practices and help build trust with stakeholders. Trustworthiness in the hardfacing process is bolstered through rigorous testing and quality control measures. Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic or dye penetrant testing, are routinely employed to identify any potential defects or discontinuities in the hardfaced layer. By ensuring the integrity of the hardfacing application, manufacturers can assure clients of the product's reliability and performance. Manufacturers are now leveraging advanced technologies, including robotic automation and computer-aided welding, to enhance the precision and consistency of hardfacing processes. These innovations contribute to the overall reliability and effectiveness of hardfacing applications on stainless steel, further solidifying the process's standing in industrial maintenance strategies. Ultimately, hardfacing stainless steel is an amalgamation of art and science, where practical experience and analytical expertise converge to prolong the life of critical components. By adhering to industry standards, embracing technological advancements, and maintaining rigorous quality control, the process not only significantly extends the service life of stainless steel components but also maximizes cost-efficiency and performance for a wide array of industrial applications.
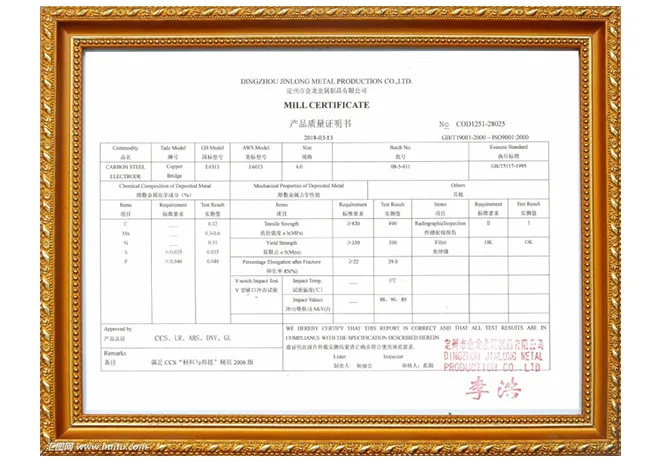

To establish authoritativeness in hardfacing stainless steel, it's crucial to rely on industry standards and guidelines, such as those provided by the American Welding Society (AWS). Compliance with these standards ensures not only the quality and safety of the hardfacing application but also enhances its performance. Documentation and adherence to these guidelines demonstrate a commitment to best practices and help build trust with stakeholders. Trustworthiness in the hardfacing process is bolstered through rigorous testing and quality control measures. Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic or dye penetrant testing, are routinely employed to identify any potential defects or discontinuities in the hardfaced layer. By ensuring the integrity of the hardfacing application, manufacturers can assure clients of the product's reliability and performance. Manufacturers are now leveraging advanced technologies, including robotic automation and computer-aided welding, to enhance the precision and consistency of hardfacing processes. These innovations contribute to the overall reliability and effectiveness of hardfacing applications on stainless steel, further solidifying the process's standing in industrial maintenance strategies. Ultimately, hardfacing stainless steel is an amalgamation of art and science, where practical experience and analytical expertise converge to prolong the life of critical components. By adhering to industry standards, embracing technological advancements, and maintaining rigorous quality control, the process not only significantly extends the service life of stainless steel components but also maximizes cost-efficiency and performance for a wide array of industrial applications.
Related Video
Copyright © 2025 Dingzhou Jinlong Metal Production Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sitemap | Privacy Policy




























